4 多线程经典问题(生产者-消费者)
“生产者——消费者”问题是Linux多线程编程中的经典问题,主要是利用信号量处理线程间的同步和互斥问题。
“生产者——消费者”问题描述如下:
有一个有限缓冲区(这里用有名管道实现 FIFO 式缓冲区)和两个线程:生产者和消费者,它们分别不停地把产品放入缓冲区中拿走产品。一个生产者在缓冲区满的时候必须等待,一个消费者在缓冲区空的时候也不IXUS等待。另外,因为缓冲区是临界资源,所以生产者和消费者之间必须互斥进行。它们之间的关系如下:

这里要求使用有名管道来模拟有限缓冲区,并用信号量来解决“生产者——消费者”问题中的同步和互斥问题。
4.1信号量分析
这里使用3个信号量,其中两个信号量 avail 和 full 分别用于解决生产者和消费者线程之间的互斥问题。其中avail 表示缓冲区的空单元数,初始值为N;full 表示缓冲区非空单元数,初始值为 0 ; mutex 是互斥信号量 ,初始值为 1(当然也可以用互斥锁来实现互斥操作)。
4.2画出流程图
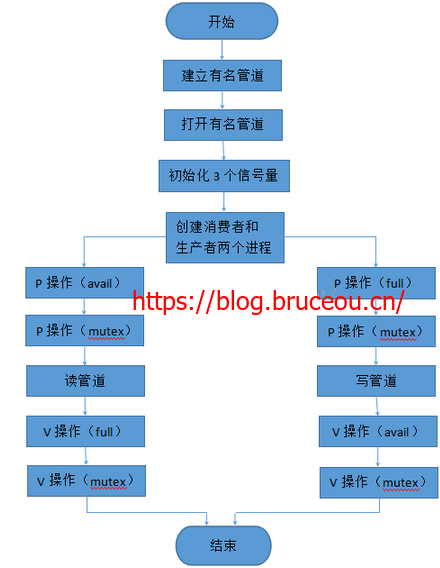
4.3编写代码
本实验的代码中缓冲区拥有3个单元,每个单元为5个字节。为了尽量体现每个信号量的意义,在程序中生产过程和消费过程是随机(采取0~5s 的随机事件间隔)进行的,而且生产者的速度比消费者的速度平均快两倍左右。生产者一次生产一个单元的产品(放入hello字符串),消费者一次消费一个单元的产品。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define MYFIFO "myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE 3
#define UNIT_SIZE 5
#define RUN_TIME 30
#define DELAY_TIME_LEVELS 5.0
void *producer(void *arg);
void *customer(void *arg);
int fd;
time_t end_time;
sem_t mutex,full,avail;
int main()
{
int ret;
pthread_t thrd_prd_id,thrd_cst_id;
srand(time(NULL));
end_time = time(NULL) + RUN_TIME;
/*创建有名管道*/
if((mkfifo(MYFIFO,0644) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
{
perror("mkfifo error!");
exit(-1);
}
/*打开管道*/
fd = open(MYFIFO,O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1)
{
perror("open fifo error");
exit(-1);
}
/*初始化互斥信号量为1*/
ret = sem_init(&mutex,0,1);
/*初始化avail信号量为 N */
ret += sem_init(&avail,0,BUFFER_SIZE);
/*初始化full信号量为0*/
ret += sem_init(&full,0,0);
if(ret != 0)
{
perror("sem_init error");
exit(-1);
}
/*创建两个线程*/
ret = pthread_create(&thrd_prd_id,NULL,producer,NULL);
if(ret != 0)
{
perror("producer pthread_create error");
exit(-1);
}
ret = pthread_create(&thrd_cst_id,NULL,customer,NULL);
if(ret != 0)
{
perror("customer pthread_create error");
exit(-1);
}
pthread_join(thrd_prd_id,NULL);
pthread_join(thrd_cst_id,NULL);
close(fd);
unlink(MYFIFO);
return 0;
}
void *producer(void *arg) //生产者线程
{
int real_write;
int delay_time;
while(time(NULL) < end_time)
{
delay_time = (int)(rand() * DELAY_TIME_LEVELS/RAND_MAX/2.0) + 1;
sleep(delay_time);
/*P操作信号量avail和mutex*/
sem_wait(&avail);
sem_wait(&mutex);
printf("\nproducer have delayed %d seconds\n",delay_time);
/*生产者写入数据*/
if((real_write = write(fd,"hello",UNIT_SIZE)) == -1)
{
if(errno == EAGAIN)
{
printf("The buffer is full,please wait for reading!\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("producer writes %d bytes to the FIFO\n",real_write);
printf("Now,the buffer left %d spaces!\n",avail);
}
/*V操作信号量full 和 mutex*/
sem_post(&full);
sem_post(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *customer(void *arg) //消费者线程
{
unsigned char read_buffer[UNIT_SIZE];
int real_read;
int delay_time;
while(time(NULL) < end_time)
{
delay_time = (int)(rand() * DELAY_TIME_LEVELS/RAND_MAX/2.0) + 1;
sleep(delay_time);
sem_wait(&full); //P操作信号量full和mutex
sem_wait(&mutex);
memset(read_buffer,0,UNIT_SIZE);
printf("\nCustomer have delayed %d seconds\n",delay_time);
if((real_read = read(fd,read_buffer,UNIT_SIZE)) == -1)
{
if(errno == EAGAIN)
{
printf("The buffer is empty,please wait for writing!\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("customer reads %d bytes from the FIFO\n",real_read);
}
sem_post(&avail); //V操作信号量 avail 和 mutex
sem_post(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
} 执行结果如下:
$ ./cust_prod
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 3 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 3 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 1 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
Customer have delayed 1 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 3 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 1 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 1 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 1 spaces!
Customer have delayed 3 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
Customer have delayed 1 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 3 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
producer have delayed 1 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 1 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
Customer have delayed 1 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 3 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces!
Customer have delayed 2 seconds
customer reads 5 bytes from the FIFO
producer have delayed 2 seconds
producer writes 5 bytes to the FIFO
Now,the buffer left 2 spaces! 